ABOUT THE DISEASE
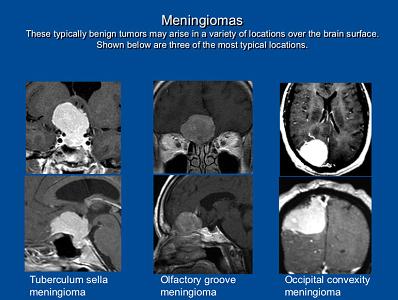
A tumor that forms on membranes covering the brain and spinal cord inside the skull is referred to as meningioma. The tumor particularly forms on the meninges—the three layers of membranes. These tumors usually grow slowly. Most tumors, almost 90% are not cancerous (benign).
Majority of meningiomas occur in the brain, but some may also grow on the spinal cord as well.
SYMPTOMS
Most meningiomas grow at a slow pace and symptoms often develop gradually. The most common symptoms include:
- • Headaches
- • Seizures
- • Blurred vision
- • Weakness in arms or legs
- • Numbness
- • Speech problem
CAUSES
The causes of meningioma are not completely clear but can be due to the following factors:
• Exposure to radiation
• Neurofibromatosis type 2 (genetic disorder)
• Any previous injury
• Skull fractures
DIAGNOSIS
Meningiomas are rarely diagnosed before symptoms begin to appear. The following tests are used to diagnose meningioma
- Clinical Evaluation
- A brain scan: an MRI and/or a CT scan.
- Biopsy
- Imaging tests PET scan, Cerebral angiogram, EEG, X-ray
TREATMENT METHODS
Observation is often recommended in case the tumor is not causing any symptoms. In order to find out if the tumor is growing, brain scans are performed regularly.
Surgery may be required if the growth of the tumor is likely to cause problems or if symptoms begin to arise.
You may also like to learn about:
Brain tumor
Glioma
Seizures
Astrocytoma
Pituitary disorders
Glioblastoma multiforme(GBM)