ABOUT THE DISEASE
An abnormal growth of cells in the brain causes brain tumours. The tumours can be broadly divided into two categories: benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). Benign brain tumours grow and press on nearby areas of the brain. They rarely spread into other tissues and may recur (come back). Malignant brain tumours are likely to grow quickly and spread into other brain tissue.
The tumours can either originate from the brain (primary tumours), or can originate from any other part of the body and then spread to the brain (metastatic tumours). Metastatic tumours are more common.
The tumours are graded from grade I to grade 4 depending upon the cell kind and other characteristics such as speed of growth, tendency to spread, etc.
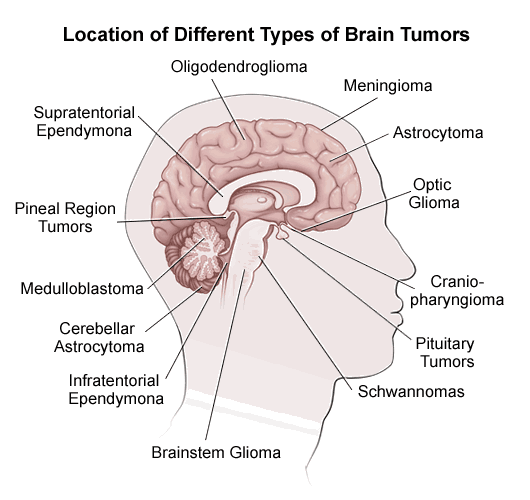
Some of the types of brain tumors are: Glioma, Meningioma, Schwannoma, Ependymoma, Craniopharyngioma, Pituitary tumors, etc.
SYMPTOMS
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Double vision
- Change in alertness
- Changes in hearing
- Changes in taste or smell
- Memory loss
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty writing or reading
- Dizziness or abnormal sensation of movement (vertigo)
- Loss of balance
- Loss of coordination
- Changes in mental function
- Muscle weakness in the face, arm, or leg (usually on just one side)
- Numbness or tingling on one side of the body
- Personality, mood, behaviour, or emotional changes
CAUSES
The causes of brain tumours is unknown however their chances are increased when associated with certain factors / diseases like ::
-Radiation therapy
-Some inherited conditions like neurofibromatosis, Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, and Turcot syndrome.
DIAGNOSIS
- Physical examination
- CT Scan
- MRI
- PET Scan
- EEG
- CSF examination
TREATMENT METHODS
Generally three kinds of treatment options are recommended based on the kind, size and location of tumours. Some medications are also prescribed esp in the case of primary tumours in kids.
- Brain tumor surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
You may also like to learn about:
Pituitary tumor
Astrocytoma
Glioma
Neurofibromatosis
Parkinsons disease
Acoustic neuroma