IMPORTANCE OF GOLDEN HOUR IN ISCHAEMIC STROKE
The benefit of tPA, tissue plasminogen activator (thrombolytic therapy) in acute ischemic stroke is strongly time dependent, being maximal in the first minutes after stroke and declining steadily during the first three hours. Patients who present within the first 60 minutes after symptom onset have the greatest opportunity for benefit from treatment.
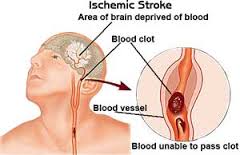
There are two types of strokes: hemorrhagic or ischemic. An Ischaemic stroke occurs as a result of an obstruction within a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain, accounting for approx 87% of all stroke cases. A Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures and spills blood into brain tissue. The most common cause for the rupture are uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure),aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). Treatment differs depending on the type of stroke.
An ischemic stroke may happen in two ways:
- Thrombotic stroke: A clot (thrombus) may form in an artery that is already very narrow. If it completely blocks the artery, it causes a stroke.
- Embolic stroke: A clot may break off from another place in the blood vessels of the brain, or some other part of the body, and travel up to the brain to block a smaller artery. This is called an embolism.
Non-modifiable risk factors for stroke:
- Family history
- Age
- History of prior stroke, TIA or heart attack
Modifiable risk factors for stroke:
- High blood pressure
- Cardiovascular disease
- Cigarette smoking
- Carotid artery disease
- Diabetes
- Undesirable blood cholesterol levels
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise and physical activity
Common symptoms of ischemic stroke are:
- Sudden weakness of a leg, arm or one side of the face
- Sudden trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden vision problems, such as blurred or double vision
- Sudden loss of coordination or problems with balance
- Sudden numbness, weakness or dizziness
F A S T rule can be followed:
F- Face- ask the person to smile-Does one side of the face droop?
A -Arm- ask the person to raise both hands. Does one arm drift downwards?
S - Speech- ask the person to repeat a sentence. Is the speech slurred?
T - Time-If the person has any of these symptoms, send him to a stroke unit immediately.
Treatment:
Mostly strokes are ischemic and are commonly caused by blood clots that interrupt blood flow in an area of the brain. A clot-busting drug (thrombolytic therapy) may be given to dissolve the clot in these patients. The drug breaks up blood clots and helps restore blood flow to the ischemic area. This drug is the only approved acute stroke treatment for clot-related, or ischemic stroke and has been shown to reduce stroke-related disability. However, it is only approved for use within three hours of symptom onset, the Golden window.
Prior to it, patients must undergo blood and radiological investigations, including a brain scan to ensure the stroke is ischemic and not haemorrhagic.
The golden window is often missed due to delays in seeking treatment, resulting from lack of awareness about stroke signs and symptoms. It is important to realize that for every minute in which blood flow is not restored, nearly 2 million additional nerve cells die.
A stroke is a medical emergency. Immediate treatment can save lives and reduce disability.
To know more about the latest update on this treatment protocol and treating centers offering the same as well as
for getting your reports reviewed, post a query
