ABOUT THE DISEASE
Thalassemia is an inherited disease i.e. passed through generations in which the body produces abnormal kind of haemoglobin (the protein in red blood cells, responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs). The disease affects the body`s capacity to produce Red Blood cells and haemoglobin, thereby causing anemia.
SYMPTOMS
No symptoms are apparently visible in the case of minor thalassemia, however children with major thalassemia show prominent symptoms (as below) during the first two years itself. A severe form of thalassemia (alpha thalassemia major) can even cause stillbirth.
- Pale skin
- Low energy or lethargy
- Shortness of breath
- Lack of appetite
- Dark urine
- Jaundice
- Slow growth and delayed puberty
- Bone deformities in the face
Untreated thalassemia major can cause heart failure and infection.
CAUSES
Thalassemia is caused when one inherits a missing or damaged gene from one or both the parents. There are two forms of such inherited thalassemia:
- • Thalassemia minor : occurs when the problem is inherited from only one parent. This does not lead to any symptoms and therefore is known as being a "silent carrier" of thalassemia.
- • Thalassemia major : develops when the problem is inherited from both parents. If both of the parents are carriers, one has a 25% risk of having the kind of thalassemia that will cause symptoms.
There are two kinds of Thalassemia (alpha and beta) depending upon the kind of protein that is missing or damaged. Both these kinds can exist in any of the two forms (minor or major).
DIAGNOSIS
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Haemoglobin electrophoresis
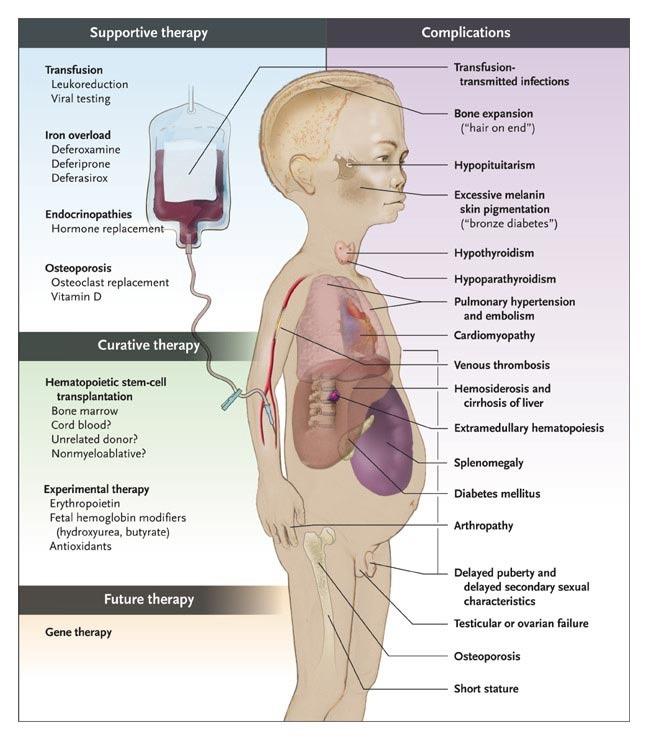
TREATMENT METHODS
The treatment comprises of regular blood transfusion and folate supplements.
Bone marrow transplant is one of the most effective treatments (especially in the case of children).
You may also like to learn about:
Sickle cell Anemia
Anemia Aplastic
Anemia Iron deficiency
Anemia Hemolytic
Leukemia
Purpura