Also known as Chronic Renal disease, Chronic kidney disease, Chronic Renal Failure.
ABOUT THE DISEASE
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs that are located at the back, on either side of spine, just underneath the rib cage. They are about as big as a fist and are responsible for making urine by filtering wastes and extra water out of the body. The kidneys also produce certain necessary hormones (erythropoietin, renin, and calcitriol) and help in regulating blood pressure by producing life-sustaining chemicals.
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney functioning over time. Losing their ability to filter enough waste products from the blood, they also lose the ability to regulate the body`s balance of salt and water. Eventually, the kidneys slow their production of urine or stop producing it completely. This can lead to a life-threatening overload of fluids. It can also lead to a dangerous build up of waste products in the blood. These changes can affect the functioning of the heart (heart failure) and brain.
SYMPTOMS
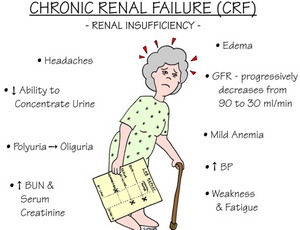
The symptoms take time to develop and include:
- • Headache
- • Weakness and fatigue
- • Itching and dry skin
- • Vomiting
- • Pale skin
- • Slowing of growth in children
- • Tiredness
- • Poor appetite
- • Increased thirst
- • High blood pressure
- • Bone damage in adults
- • Swelling of feet and hands (edema)
- • Sleep problems - insomnia
- • Low drive for sex
CAUSES
High blood pressure (hypertension) and diabetes are the two most common causes.
Other common factors include:
- Polycystic kidney disease.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Alport syndrome.
- The flow of urine out of the kidney is blocked (obstructive uropathy).
- Long-term exposure to lead, mercury, and other chemicals and medicines.
- Kidney stones with infection.
- Reflux nephropathy.
- Pain medicine overuse.
DIAGNOSIS
- Measuring blood pressure
- Urine Test for the presence of albumin or other proteins
- Serum creatinine to calculate glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Blood urea nitrogen
- Serum electrolytes
- Imaging tests-Ultrasound/MRI/CT scan
TREATMENT METHODS
- Antihypertensive medication
- Low-protein and low-salt diet
- Reduced fluid intake
- Controlling blood sugar
- Regular exercise
- In case the disease is not controlled in time it might lead to a need for Dialysis or a Renal Transplant.
You may also like to learn about:
Renal failure acute
Kidney cancer
Kidney stones/calculi
Polycystic kidney
Hydronephrosis
Glomerulonephritis