ABOUT THE DISEASE
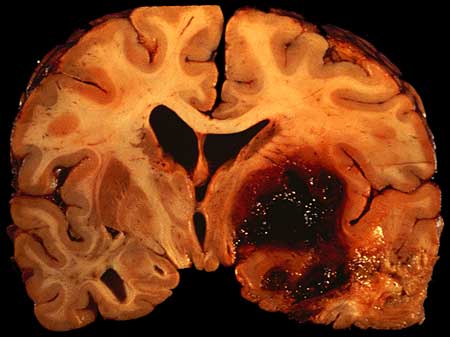
A brain hemorrhage is a life threatening condition caused by bleeding within the brain tissue, sometimes leading to hemorrhagic stroke, when the brain is deprived of oxygen due to an interruption of its blood supply.
It can occur as bleeding:
- Inside the brain
- Between the brain and the membranes that cover it
- Between the layers of the brain`s covering
- Between the skull and the covering of the brain
SYMPTOMS
These include:
- • Sudden headache
- • Steadily increasing neurologic losses such as weakness, inability to move, numbness
- • Difficulty in speaking or hearing
- • Problems in vision, eyelid drooping, double vision or uncontrolled eye movements
- • Nausea and vomiting
- • Seizures
- • Loss of consciousness
CAUSES
Some of the main causes and risk factors are:
- Head injury
- Abnormalities in blood vessels - such as aneurysm or vascular malformation
- High blood pressure
- Drug usage: like cocaine and other illicit drugs
- Amyloid angiopathy
- Blood and bleeding disorders such as low platelet counts, hemophilia, leukemia etc.
DIAGNOSIS
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Cerebral Angiography
- CT Scan
- MRI Brain
- Blood tests to measure platelet counts
- Liver function tests
- PT / PTT
TREATMENT METHODS
Course of treatment is decided based on the cause, location and severity of bleeding.
It is aimed to stop the bleeding, remove the clot, and relieve the pressure on the brain. If left alone the brain will eventually absorb the clot within a couple of weeks – however the damage to the brain caused by Intra Cerebral Pressure and blood toxins may be irreversible.
Treatment may be medical or surgical. Generally, patients with small hemorrhages and minimal deficits are treated medically. Patients with cerebellar hemorrhages (>3 cm3) who are deteriorating or who have brainstem compression and hydrocephalus are treated surgically to remove the hematoma as soon as possible.
Medicines -
- Anticonvulsants to control seizures
- Corticosteroids or diuretics to reduce swelling
- Painkillers
Surgery -
- Depending on the location of the clot either a craniotomy or a stereotactic aspiration may be performed.
You may also like to learn about:
Stroke
Aneurysms
Arteriovenous malformations
Convulsions
Brain tumors
Hypertension