Also known as PTA (Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty), PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty), Balloon Angioplasty.
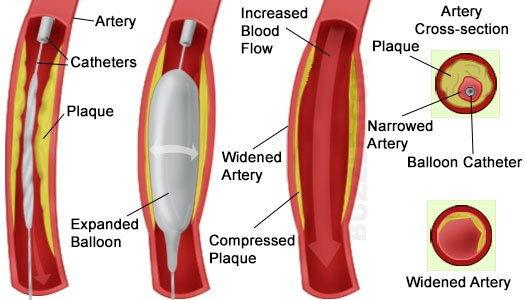
Angioplasty is a procedure done to widen the blood vessels narrowed by stenosis or occlusion, with the help of a catheter fitted with balloon and stents. Some catheters are equipped with drill (rotablator) to clean out the plaque. This helps to improve the blood supply to the heart muscle and is advised to patients with angina, coronary artery disease, heart attack.
PROCEDURE
It is done in Cardiac Catheterization Lab, under sedation, using fluoroscopic guidance and contrast media. Angiography is done before this procedure to know the location and extent of blockages. A catheter (thin, flexible, hollow tube) with a small inflatable balloon is inserted through an artery in the groin or arm. It is directed upto the heart and into the coronary artery until its tip reaches the narrowed/blocked area. The balloon is then gently inflated to widen the vessel. A stent is already in place on balloon which expands as balloon inflates and holds open the narrowed artery. The balloon is let down and removed, leaving the stent in place. Some stents are coated with medicine that is slowly and continuously released into the artery. They are called drug-eluting stents.
DURATION
The procedure is completed in 1-2 hours. Hospital stay is of 1-3 days.
RECOVERY
Normal routine can be resumed within a week. Healthy lifestyle practices have to be followed as per the advice.
RISKS
There is a danger of puncturing the vessel with the guidewire during an angioplasty, hematoma or hemorrhage at the puncture site, heart attack, stroke, recurrence of stenosis, etc.