Also known as Angiitis, Arteritis
ABOUT THE DISEASE
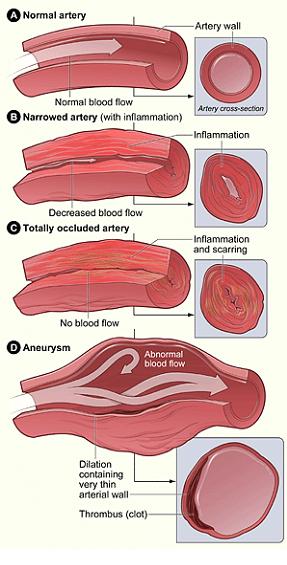
Vasculitis is an inflammation of blood vessels. It causes changes in the walls of blood vessels, including thickening, weakening, narrowing, and scarring. These changes restrict blood flow, resulting in organ and tissue damage. In vasculitis, inflammation can lead to serious problems. Complications depend on which blood vessels, organs, or other body systems are affected.
Vasculitis can affect any of the body`s blood vessels. These include arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry blood from heart to the organs. Veins carry blood from organs and limbs back to heart. Capillaries connect the small arteries and veins.
SYMPTOMS
The signs and symptoms of vasculitis vary greatly and are often related to decreased blood flow throughout the body. The common symptoms are:
- • Fever
- • Headache
- • Fatigue
- • Weight loss
- • General aches and pains
- • Night sweats
- • Rash
- • Nerve problems, such as numbness or weakness
- • Loss of a pulse in a limb
CAUSES
What causes vasculitis is not fully understood. Some types are related to a person`s genetic makeup. Others result from the immune system attacking blood vessel cells by mistake. Possible triggers for this immune system reaction include:
• Infections, such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C
• Blood cancers
• Immune system diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and scleroderma
• Reactions to certain drugs
DIAGNOSIS
- Clinical evaluation
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests such as Biopsy, Urinalysis, EKG, ECG, Echo, X-Ray, MRI, ultrasound, angiography.
TREATMENT METHODS
Treatment for vasculitis depends on the type of vasculitis someone has, which organs are affected, and how severe is the condition.
People with severe vasculitis are treated with prescription medicines. Rarely, surgery may also be required. Those having mild vasculitis may find relief with over-the-counter pain medicines, such as acetaminophen, aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen.
The main aim in the treatment of vasculitis is to reduce inflammation in the affected blood vessels. This is often done by reducing or stopping the immune response that caused the inflammation.
You may also like to learn about:
Thrombophlebitis
Vascular disorders
Inflammation
Purpura
Ulcer
Haemorrhage