ABOUT THE DISEASE
TB is an infection caused by a bacterium called mycobacterium tuberculosis.
It usually affects the lungs however it can spread to other parts as well such as the joints, bladder, spine, brain (tubercular meningitis), bones and many others.
TB that affects the lungs is the only form of the condition that is contagious, however usually only spreads after prolonged exposure to someone with the illness.
In most healthy people, the immune system (the body`s natural defence against infection and illness) kills the bacteria. However, sometimes the immune system cannot kill the bacteria, allowing it to remain in body but manages to prevent it from spreading. This is known as latent TB.
If the immune system fails to kill or contain the infection, symptoms will develop within a few weeks or months. This is known as active TB.
Latent TB could develop into an active TB infection at a later date, particularly if the immune system weakens due to any reason.
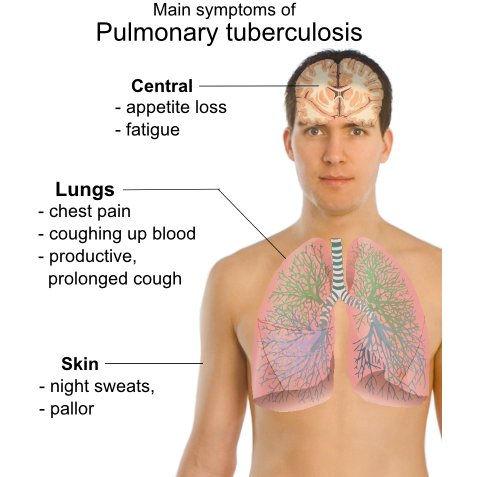
SYMPTOMS
Some of the symptoms associated with active TB are:
- • Cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer, and can bring up blood
- • Chest pain
- • Fever
- • Fatigue
- • Unintended weight loss
- • Loss of appetite
- • Chills and night sweats
- • Joint Pain (if TB affects the joints)
- • Blood in urine along with pain during urination (If TB affects the bladder)
- • Headache and nausea (Brain TB)
- • Back pain and leg paralysis (TB of the spine)
CAUSES
Bacteria that cause the disease are inhaled in the form of microscopic droplets expelled into the air, that come from a person with tuberculosis, while coughing, speaking or sneezing. They dry out quickly, but the bacteria itself can remain airborne for hours.
However, the tuberculosis bacteria are killed when exposed to ultraviolet light, including sunlight.
Non-Lung TB can be caused due to ingestion of infected milk or dairy products which set up infections in the gastro-intestinal tract and also affect the reproductive systems in men and women.
DIAGNOSIS
- Montaux test
- Chest x-ray
- Sputum examination
- Quantiferon-TB Gold test
TREATMENT METHODS
This disease is completely curable by taking a course of antibiotics, usually for six to nine months.
Several different antibiotics are used in combination, mainly Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol and Pyrazinamide. No medicines should be skipped in between. If the treatment is stopped in between it can lead to a drug-resistant form of TB, extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR- TB) or Mult drug resistant i.e MDR-TB, which is a very serious situation for which treatment can last as long as 18 months.
Side effects include a skin rash, an upset stomach or liver disease.
Alcohol consumption or taking acetaminophen while taking this treatment is to be avoided because this can damage the liver. Always check with your doctor before you take any other medicine because some drugs interact with these drugs and can cause side effects.
BCG Vaccination can provide effective protection against the disease.
You may also like to learn about:
Lung cancer
Pneumonia
Hemoptysis
Interstitial lung disease
Bronchitis
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease