Also known as Nearsightedness
ABOUT THE DISEASE
This is a refractive error where the individual has difficulty in seeing objects that are far away (blurred vision). The objects that are near are seen clearly. This disease generally affects during the pre teen years and stops progressing during the 20`s. If the disease continues to develop it is called progressive myopia.
SYMPTOMS
- Headache
- Squinting
- Eyestrain
- Fatigue
- Children commonly complain of not being able to see the blackboard in school.
DIAGNOSIS
- Refraction test
- Retinal examination
- Tonometry
- Visual acuity test
CAUSES
It results because the eyeball is too long or the cornea has too much curvature, so the light entering the eye is not focused correctly. Images focus in front of the retina rather than on it, causing blurred vision.
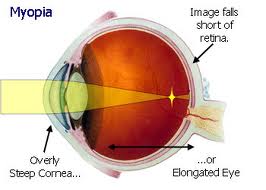
This is generally hereditary, however some of the following factors can also cause the disease:
- Growth spurts in children.
Secondary Myopia can happen from other medical conditions such as:
- Cataracts.
- Uncontrolled diabetes.
- Pregnancy.
- Premature birth.
TREATMENT METHODS
- Glasses or contact lenses
The prescription for glasses or contact lens is a negative number, such as -2..00. The higher the number, the stronger the lenses will be.
- Refractive surgery can eliminate dependence on glasses or contact lenses. The most common procedures for myopia are performed with a laser, called: LASIK surgery.
You may also like to learn about:
Hypermetropia
Eye stroke
Eye infections
Eye strain
Vision impairment/blindness
Color blindness