ABOUT THE DISEASE
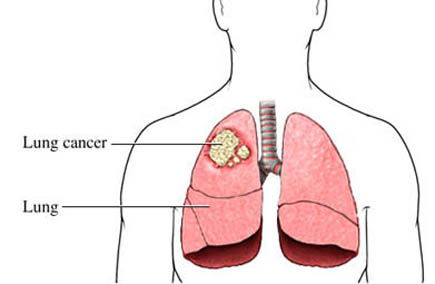
Lung cancer is a cancerous tumor that originates from the lungs. If the cancer started somewhere else in the body and spread to the lungs, it is called metastatic lung cancer.
The lungs are located in the chest. When we breathe, air travels through nose, down the windpipe (trachea), and into the lungs, where it spreads through tube like structures called bronchi. Most lung cancers begin in the cells that line these tubes.
There are two main types of lung cancer: Non small cell lung cancer - NSCLC (most common) or Small cell lung cancer.
Following are the three main types of Non small cell lung cancer:
1. Adenocarcinoma often starts growing near the outside surface of the lung and may vary in both size and growth rate. This is the most common type of lung cancer
2. Squamous cell carcinoma usually starts in one of the larger breathing tubes near the center of the chest. The size of these lung tumors can range from very small to quite large.
3. Large cell carcinoma often starts near the surface of the lung, grows rapidly and is usually quite extensive when diagnosed.
Lung cancer is the most common malignancy worldwide, with more than 1 million cases diagnosed yearly.
SYMPTOMS
- • Cough
- • Shortness of breath or wheezing.
- • Coughing up blood - hemoptysis.
- • Chest pain.
- • Hoarseness.
- • Swelling of the face.
- • Drooping eyelid.
- • Anemia.
- • Weight loss.
- • Facial paralysis (later stages)
CAUSES
This cancer usually starts when the lungs are exposed to harmful chemicals. Lung cancer can take several years to develop. Cigarette smoking is the most common risk factor for developing lung cancer. Although, 25% of those suffering from lung cancer have never smoked. Other risk factors are:
- Age over 65 (two thirds of all patients)
- Radon gas exposure
- Asbestos and other industrial substance exposure.
- Second hand tobacco smoke.
- Air pollution.
- Family history of lung cancer.
DIAGNOSIS
- Chest X-Ray or a CT Scan
- Bronchoscopy
- Biopsy
TREATMENT METHODS
The treatment plan depends upon the type of cancer identified and the stage of the cancer, whether it is localized or it has spread to the nearby areas or nodules.
The following treatments can be used alone or in combination:
- Lung cancer surgery: involves removing the tumor and surrounding lung tissue. It can be a limited resection, lobectomy or Pneumonectomy and Lung transplant. It can be performed as video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) as well as robotic surgery.
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
You may also like to learn about:
Cancer metastatic
Bone cancer
Pulmonary fibrosis
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Dyspnoea
Hemoptysis