ABOUT THE DISEASE
Infertility can be broadly clubbed under two categories-
Primary Infertility: When the female is not able to conceive even after one year of unprotected sex.
Secondary Infertility: Where the female has been able to get pregnant once, but is not able to do so now.
For Pregnancy to happen - First a woman must release an egg from one of her ovaries (ovulation) and then that egg must be fertilized by the male sperm. It then travels through a fallopian tube into the uterus i.e the womb, where it attaches to the wall of the uterus and grows. As for the man, he must produce enough sperm, and the sperm must be motile enough to fertilize the egg along the way, at the proper time. Finally the fertilized egg must then be able to attach to the inside of the uterus. If any of these fail to happen, it leads to infertility.
CAUSES
About 30% of infertility cases are due to male related factors and 30% are due to problems with the female factors. Other cases are due to a combination of male and female factors (10%) or due to unknown causes (25-30%).
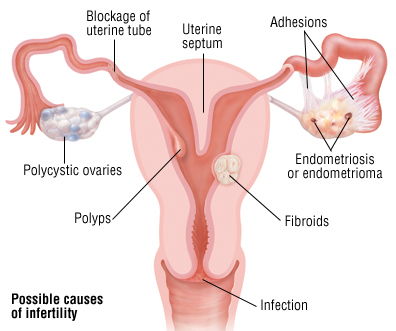
Causes for infertility in women could be:
- Problems with ovulation (Most common reason), as evidenced in females with irregular menstrual periods or no periods at all; lifestyle factors (such as stress, diet, or athletic training or alcohol or drug intake - which can affect hormonal balance); Polycystic ovary syndrome; hormonal imbalance as a pituitary gland tumor, thyroid disorder.
- Age- Fertility begins to decrease in women in the early 30s and gets worse after 35
- Pelvic infections
- Blocked fallopian tubes due to pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, or surgery for an ectopic pregnancy or any pelvic or abdominal surgery causing adhesions.
- Fibroid tumors or polyps of the uterus.
- Congenital abnormalities of the uterus
- Cervicitis - Infection of the cervix
- Cervical stenosis
- Abnormal cervical mucus.
DIAGNOSIS
It requires examination of both the partners.
For Females the tests include:
- Checking for ovulation
- Hormone levels, eg. FSH, LH, Testosterone, Thyroid
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Hysterosalpingogram
- Laparoscopy
- Endometrial biopsy
- Hysteroscopy
TREATMENT METHODS
Treatment plan completely depends upon the problem identified and might just require a lifestyle modification (stopping drinks, drugs and smoking) or counselling or medications, however in other cases a surgical intervention might be required.
- Fertility enhancing drugs may be used for women with ovulation problems.
- Surgery may be needed to repair damage to a woman`s ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, or uterus, as in endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes or polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI) of sperm, timed with ovulation.
- IVF - In Vitro Fertilization
Last but not the least, ovulation occurs about 2 weeks before the next menstrual cycle (period) starts. If a woman gets her period every 28 days, the couple should have sex between the 10th and 18th day after the period starts, to maximize chances of pregnancy.
You may also like to learn about:
Varicocele
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Endometriosis
Blocked Fallopian tubes
Azoospermia
Polycystic ovarian disease