ABOUT THE DISEASE
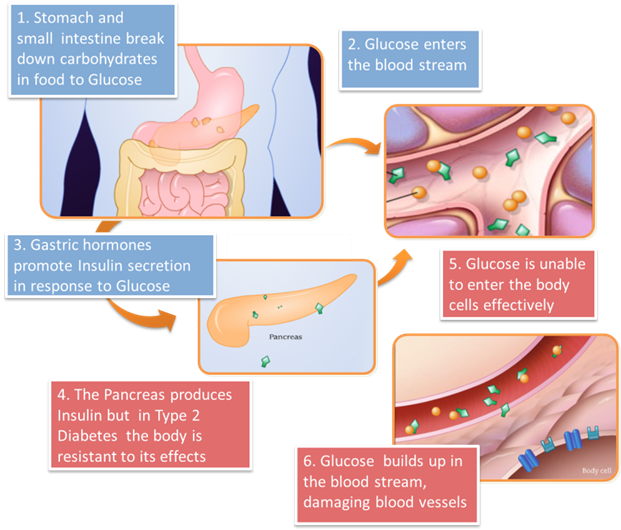
Diabetes is a chronic disease in which there is high level of sugar in the blood that occurs when a person`s body doesn`t make enough of the hormone insulin or can`t use insulin properly. For the normal human cells to generate energy from food, a process called metabolism takes place. Here the blood flowing in the vessels transports the sugar from where it is either taken in (the stomach) or manufactured (in the liver) to the cells where it is used (muscles) or where it is stored (fat). However, sugar cannot go into the cells by itself. The pancreas releases insulin into the blood, which serves as the helper, that lets sugar into the cells for use as energy.
When sugar leaves the bloodstream and enters the cells, the blood sugar level is lowered. Without insulin, sugar cannot get into the body`s cells for use as energy. This causes sugar to rise. Too much sugar in the blood is called "hyperglycemia" (high blood sugar) or diabetes.
There are 2 types of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas produces little insulin or no insulin at all. (Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas that helps the body use sugar for energy.)
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the pancreas make insulin, but this insulin does not work as it should. This condition is called insulin resistance.
Between 90% and 95% of people who are diagnosed with diabetes have type 2 diabetes.
There are some other forms of diabetes as -gestational diabetes, that develops at any time during pregnancy in a woman who does not have diabetes; due to surgery; certain medicines, etc.
Too much glucose in the blood can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease and damage to the nerves and kidneys. These are known as diabetic complications and include -
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic Nephropathy
India is called as diabetes capital of the world with over 50 million patients and approximately 9% of the population expected to be affected by this disease by 2030.
SYMPTOMS
No symptoms might be noticed in the early stages of diabetes, but damage may already be happening to the eyes, kidneys and cardiovascular system. Type 2 diabetes typically develops slowly, whereas type 1 diabetes develops over a short period. Some of the common symptoms include the following:
- • Extreme hunger
- • Extreme thirst
- • Frequent urination
- • Unexplained weight loss
- • Fatigue or drowsiness
- • Blurry vision - when the eyes start getting affected
- • Slow-healing wounds, sores or bruises
- • Dry, itchy skin
- • Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet - when the nerves get affected
- • Frequent or recurring skin, gum, bladder or vaginal yeast infections
- • When the cardiovascular system gets affected it leads to high blood pressure, cholesterol & heart problems
- • It can also cause skipped or absent periods in teen girls and women.
CAUSES
Following are some of the risk factors associated with this disease:
- Weight i.e Obesity is the single most important risk factor for type 2 diabetes. The more overweight you are, the more resistant your body is to insulin.
- Age :- The risk for type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45 years of age.
- Family history :- The risk for diabetes is higher if mother, father or sibling has diabetes.
- Race/ethnic background :- Some ethnic groups have a higher risk of diabetes than others.
- Exercise :- An inactive lifestyle is a major contributor for the disease. A minimum of 30 to 60 minutes of exercise most days of the week goes a long way in managing / avoiding this disease.
- Diet :- A diet high in fat, calories and cholesterol increases the risk of diabetes. A healthy diet is high in fiber and low in fat, cholesterol, salt and sugar. Both what you eat and how much do you eat at a time are critical factors in managing this disease.
- Polycystic ovarian disease
- Gestational diabetes
DIAGNOSIS
- Fasting sugar blood tests or with A1c blood tests, also known as glycated hemoglobin tests. The ranges for the following tests are as follows:
| Normal | Pre-diabetes | Diabetes |
| Fasting Glucose Test | Less than 100 | 100-125 | 126 or higher |
| Random (anytime) Glucose Test | Less than 140 | 140-199 | 200 or higher |
| A1c Test | Less than 5.6% | 5.7 - 6.4% | 6.5% or higher |
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: diabetes is diagnosed if glucose level is higher than 200 mg/dL 2 hours after drinking a glucose drink.
- Urine analysisTREATMENT METHODS
Although there is no permanent cure for this disease, with proper weight, diet control and medicines along with adequate amount of exercises it can be managed quite effectively. Type 2 diabetes is controlled through some oral medicines however for Type 1 diabetes an insulin therapy is prescribed.
Sometimes people who have diabetes and are on medication may have times when their blood sugar level is too low. Low blood sugar is called hypoglycemia. Signs of hypoglycemia include the following:
- Feeling very tired
- Frequent yawning
- Being unable to speak or think clearly
- Loss of muscle coordination
- Sweating
- Twitching
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness or feeling like you`re going to pass out
- Becoming very pale
This needs to be addressed immediately and it is advised to carry at least 15 grams of a fast-acting carbohydrate with you at all times, to be used in case of hypoglycemia or an insulin reaction. The following are examples of quick sources of energy that can relieve the symptoms: Glucose biscuit, fruit juice, milk, candy, etc.
You may also like to learn about:
Diabetes Gestational
Diabetic kidney problems
Diabetic foot
Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetic neuropathy